Water Resources and Inter-State Conflict: Legal Principles and the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD)
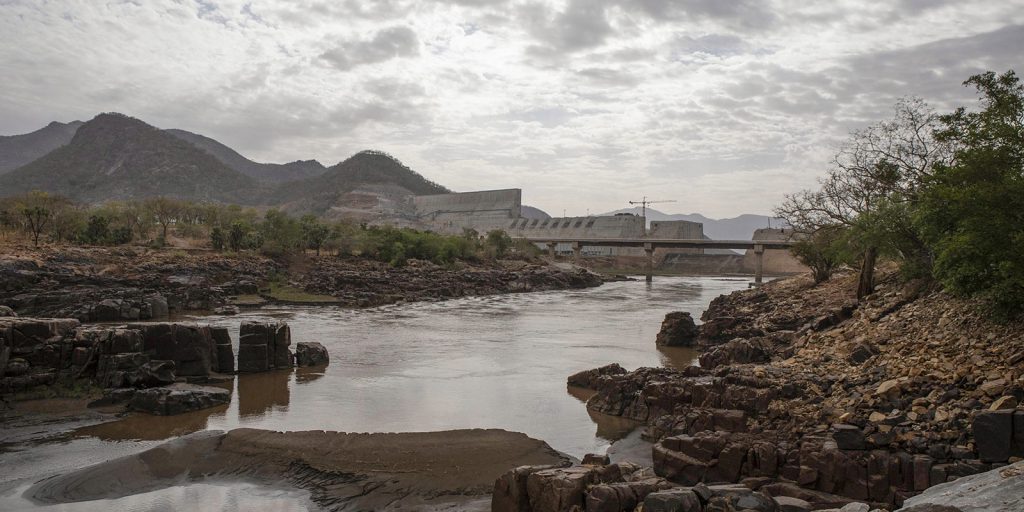
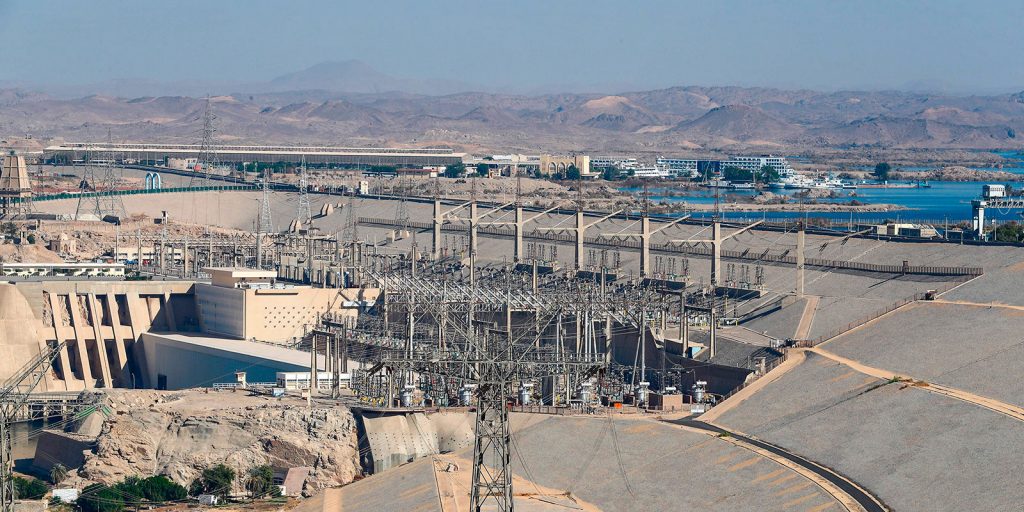
Amid the climate emergency, access to freshwater is a potential source of tension and conflict between states. One example of tension tied up to a transboundary watercourse is the on-going dispute between Egypt and Ethiopia over the water resources of the River Nile. A long-standing dispute between the countries has gained tension due to the construction of the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD) by Ethiopia.