Impact of COVID-19 on Economic, Social and State-citizens’ relations in the SADC Region
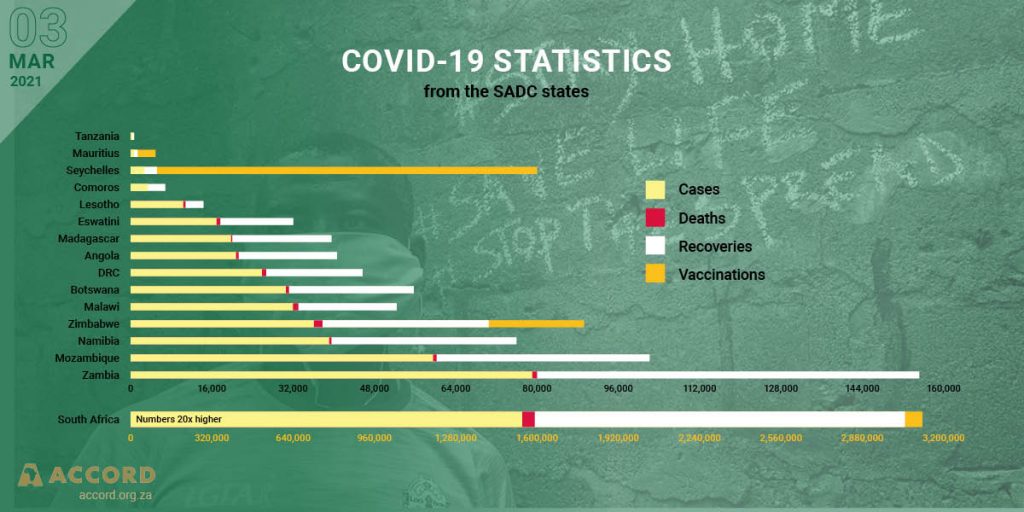
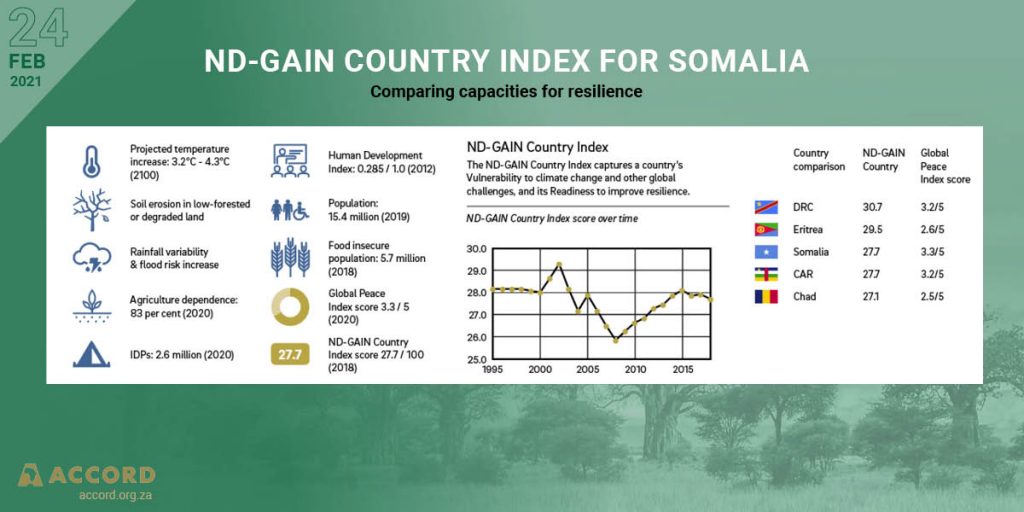
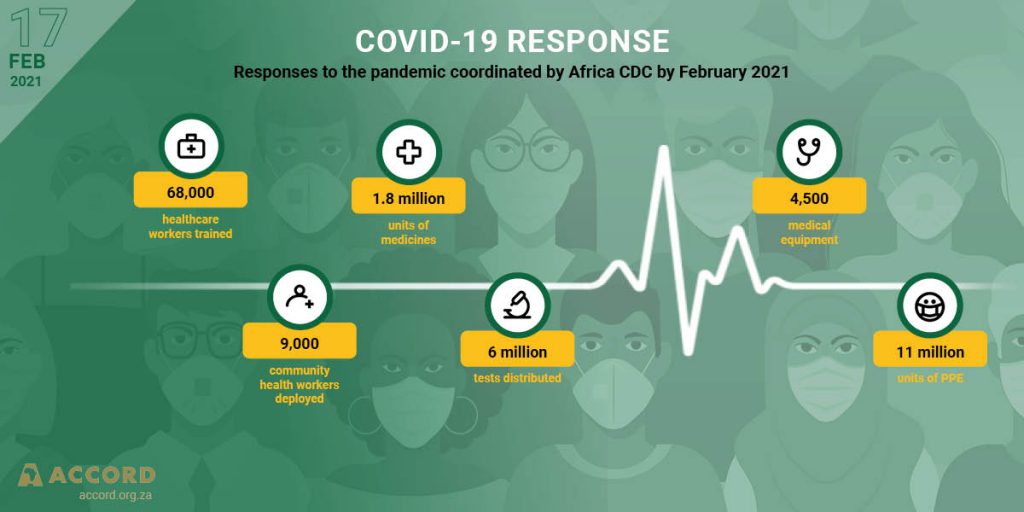
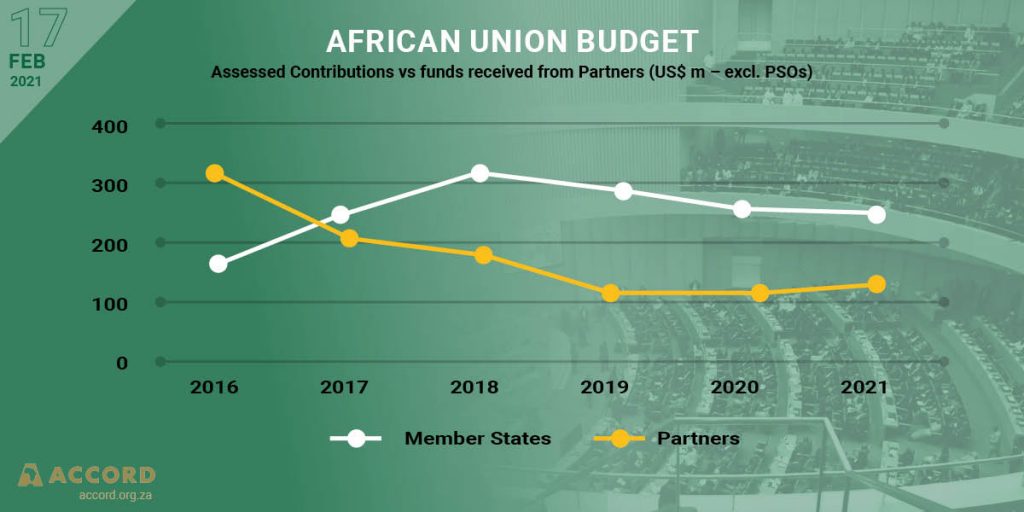
In the Southern African Development Community (SADC) Region, the pandemic has widened inequalities within, and between Member States. Labour-intensive service sectors such as retail trade, restaurants and hospitality, sports and recreation and transportation have been severely affected by measures to contain the pandemic. Activity within labour-intensive sectors are expected to remain subdued in the short to medium term. The low-skilled, low-wage workers in both formal and informal sectors are least able to withstand an economic shock. A full recovery in the labour market may take a while, worsening income inequalities and increasing poverty.