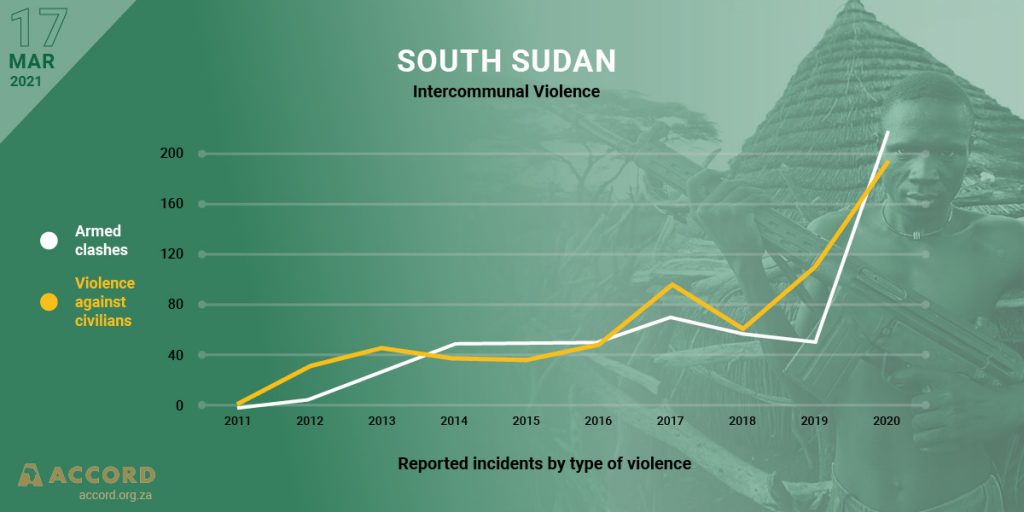
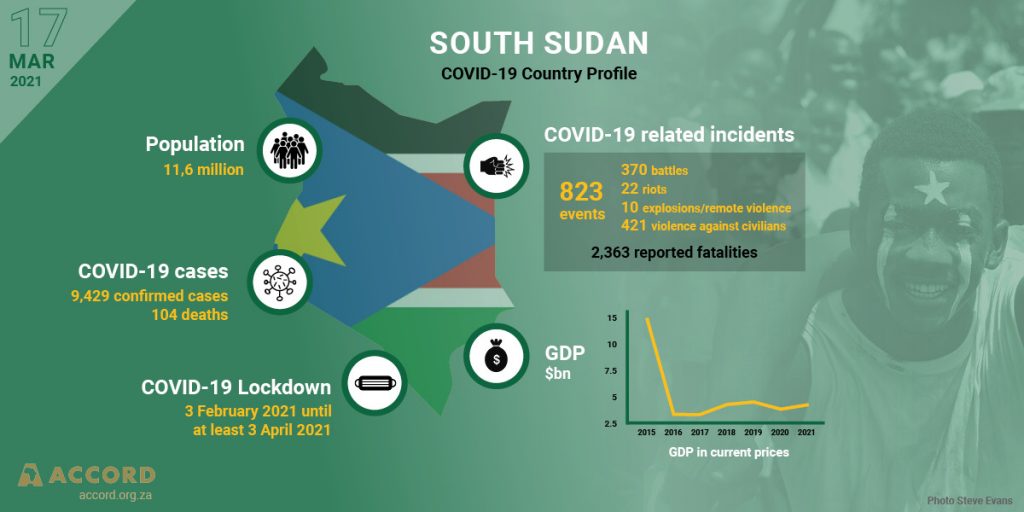
March 2021 marks a year after the executive branch of the Revitalized Government of National Unity (RTGoNU) was established partially in South Sudan at the national level. Since then the reconstituted Council of Ministers has been operationalized under the chairmanship of the President of the Republic, assisted by five Vice Presidents who represent the principal parties to the Revitalized Agreement on the Resolution of the Conflict in the Republic of South Sudan (R-ARCSS). These top political leaders were entrusted with running the machinery of the government through clusters of ministries, commissions, authorities, and independent specialized mechanisms. However, the peace process has been moving at a slow pace as key provisions of the R-ARCSS could not be implemented in time. The presence of the United Nations Mission in South Sudan (UNMISS) has become questionable too for pushing the parties into creating a conducive environment for the unification of forces, institutional reforms, humanitarian responses, return of displaced citizens, economic reforms, constitutional making, conducting population census and holding general elections towards the end of 36-month transitional period. The scourge of COVID-19 and associated restrictions have further complicated the peace process since 2020.